To expose services to the external world we have two options -
LoadBalancer - It is a service type that exposes the application in an external load balancer it distributes the requests among multiple backend services.
It is a service that points to external load balancers that are not in your Kubernetes cluster but exist elsewhere outside the cluster
This service has limitations lets say we have 10 websites hosted in your cluster and you want to expose them all to external traffic.
If you use type LoadBalancer Service you have to expose all 10 services on Cloud load balancers (each service costs money)Service provides a load-balancing mechanism but it is a simple Round-robin load-balancing algorithm It evenly distributes incoming traffic across the available pods behind the Service.
The default load-balancing algorithm is simple and effective in many cases, it may not provide advanced features such as ratio-based traffic distribution, sticky sessions, whitelisting, blacklisting, or other more advanced load-balancing strategies.

To overcome these limitations, Kubernetes provides options to integrate with more advanced load-balancing components like Ingress
2. Igress - In Kubernetes, an Ingress is the same as a load balancer service but it has some more features which are not available in load balancer. Ingress is a separate API object in Kubernetes which is not part of the Kubernetes Service resource. Ingress solves the limitation of the LoadBalancer service.
Lets say we have 10 websites hosted in your cluster and you want to expose them all to external traffic. If you use type LoadBalancer Service you have to expose all 10 services on Cloud load balancers (each service costs money) but In ingress, you just need to expose one service and it'll point to an Ingress Controller running in your cluster.
exposing multiple services to the external world using a single public IP address which is cost-effective when applications run in cloud infrastructure like AWS.

What is Ingress?
It is an object that allows traffic to come into the Kubernetes cluster. Ingress acts as a traffic controller or entry point to your cluster, allowing external traffic to reach the services running within it. The external traffic could be via HTTP or HTTPS to a service running within your Kubernetes cluster.
Internet -> Ingress -> K8s Services -> Replicas
How to setup ingress
It is a two-step process
First, we need to create an Ingress controller
Configure the Ingress resource
Ingress Controller - Ingress controller is the same as the load balancer but it has also an API gateway, Kubernetes has different types of ingress controllers to manage the resources like
NGINX ingress controller
F5
Istio
HAproxy etc.
Ingress controller is responsible for implementing the Ingress rules and handling incoming traffic. Ingress controller is not part of the control plane component we need to deploy this separately in the cluster

Set-Up Ingress controller -
Minikube v0.14.0 (and above) ships with Nginx ingress setup as an add-on . It can be easily enabled by executing
minikube addons enable ingresswith these simple step ingress controller is enabled
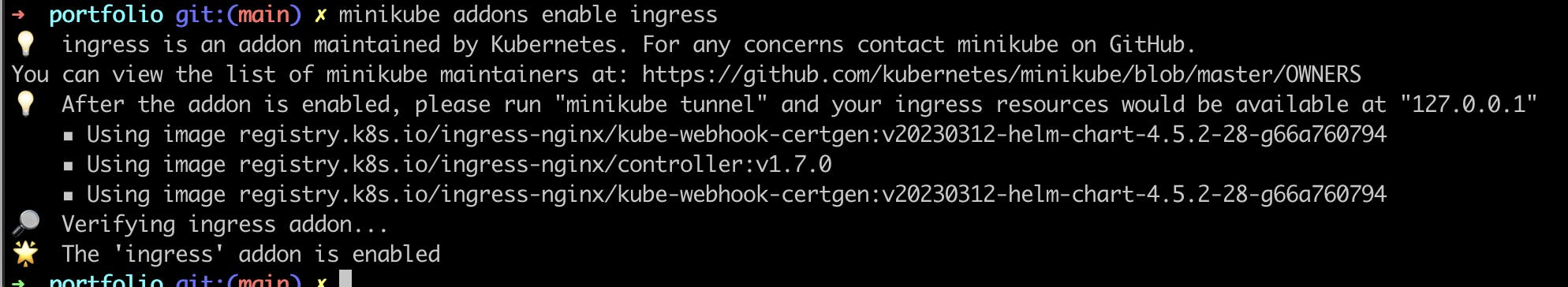
To check ingress controller is installed or not run pod command because ingress controller is pod
kubectl get pods -A | grep nginx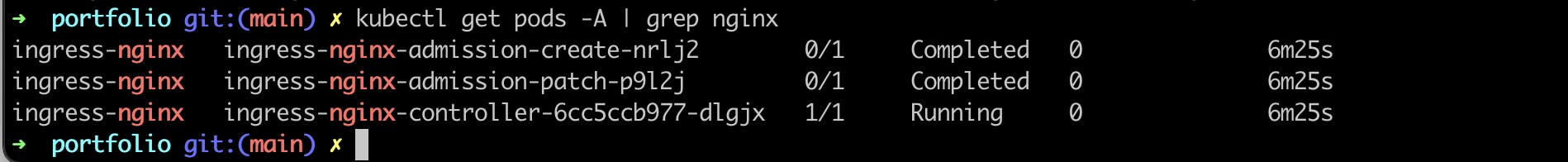
as you can see that it is running in the ingress-nginx namespace
Ingress resource - Once you successfully created Ingress controller then we can proceed with creating an Ingress resource.Ingress resources are a set of rules that define how incoming traffic should be directed to backend services. These rules can define by
1- Path-based
2- Hostname-based routing

Path-base routing - Path-based routing in Kubernetes Ingress allows you to route incoming requests to different backend services based on the URL path.
Let's say we have example.com and have two backend services running in your Kubernetes cluster: Service A and Service B. You want to route incoming requests based on the URL path to these services.
Service A handles requests for the "/app" path.
Service B handles requests for the "/api" path.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: example-ingress spec: rules: - http: paths: - path: /app pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: service-a port: number: 80 - path: /api pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: service-b port: number: 80In this example, the Ingress resource defines two rules using the
pathsfield:Requests with the path "/app" will be forwarded to Service A.
Requests with the path "/api" will be forwarded to Service B.
Host-based routing - Host-based routing in Kubernetes Ingress allows you to route incoming requests to different backend services based on the requested hostname.
It's like having different addresses for different services within a single cluster.
Let's say you have two backend services, Service A and Service B, and you want to direct requests based on the requested hostname:
Requests with the hostname "app.example.com" should go to Service A.
Requests with the hostname "api.example.com" should go to Service B.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: app.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: service-a
port:
number: 80
- host: api.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: service-b
port:
number: 80
In this example, the Ingress resource has two rules specified under rules:
Requests with the hostname "app.example.com" will be directed to Service A.
Requests with the hostname "api.example.com" will be directed to Service B.
How to create ingress resource
To create an ingress resource first you need to Create a YAML file that defines your Ingress resource rules.
save this yaml file as ingress.yaml
Apply the Ingress resource to your Kubernetes cluster by
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
You can check whether ingress resources are created or not by
kubectl get ingress
ingress resource is created
How to deploy applications using Ingress
Requirements
Kubectl configured
minikube installed
Kubernetes cluster running
Docker image
Strat the minikube cluster by
minikube startcommand.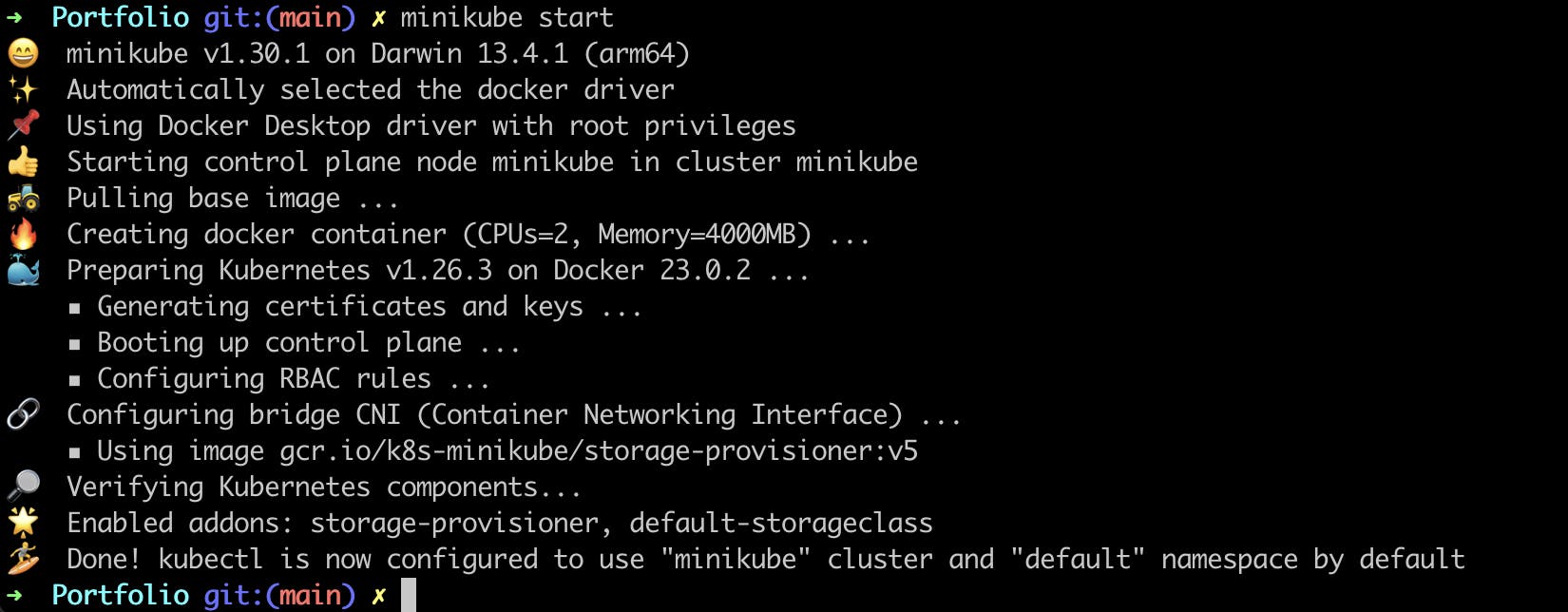
Deploy and Enable the Ingress controller
To enable the NGINX Ingress controller, run the following command
minikube addons enable ingress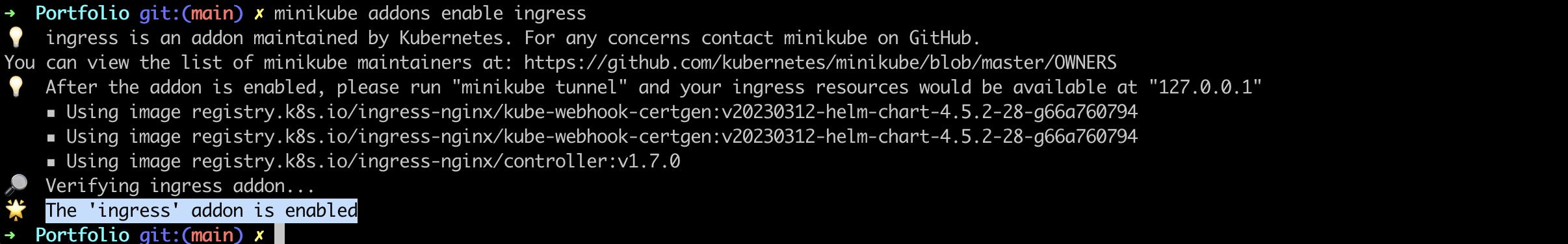
to verify ingress controller is running or not use this command
kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx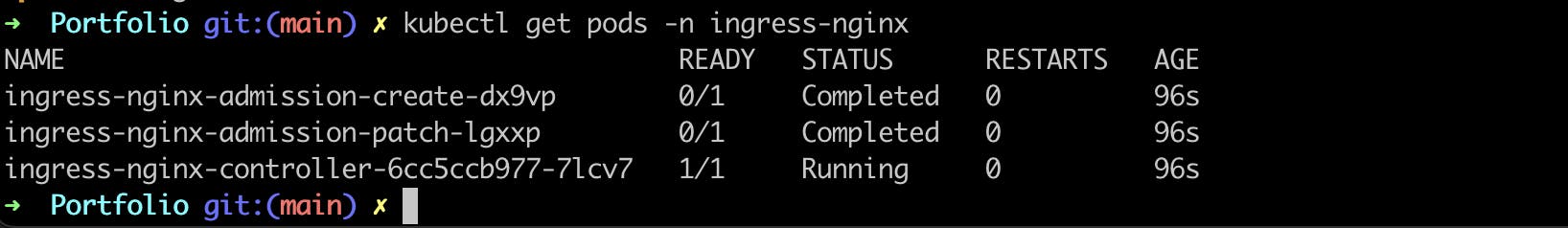
Deploy application in our cluster I am again using my own portfolio. The Docker image needs to be pulled. you can use any image of your choice.
First, i am creating deployment and service file
deployment.yaml```yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: my-portfolio labels: app: my-portfolio spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: my-portfolio template: metadata: labels: app: my-portfolio spec: containers:
- name: portfolio
image: hemantsw/portfolio
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: my-portfolio-service spec: type: NodePort selector: app: my-portfolio ports:- name: my-portfolio port: 80 targetPort: 80
- name: portfolio
Now apply this file by kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml (replace deployment with your yaml file name)

deployment and service are created parallely you can verify it by running `kubectl get deployment` and `kubectl get svc` commands

As you can see that both are running
In a few seconds, the image should be pulled & the pod should be running.
To check pods are running use this command `kubectl get pods -o wide`

4. Now, we will create an Ingress resource that will enable us to access the application.
First we need to create ingress.yaml file
```yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-portfolio-ingress
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: hemantsw.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: my-portfolio-service
port:
number: 80
In this yaml file I have set host as hemantsw.com means i can access the application with this DNS name
Now apply the yaml file by kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
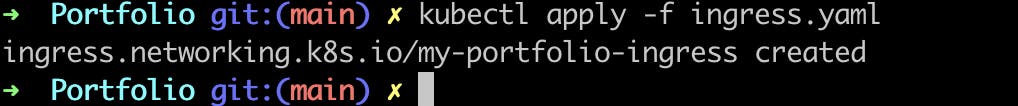
Let’s check the ingress now by kubectl get ingress command
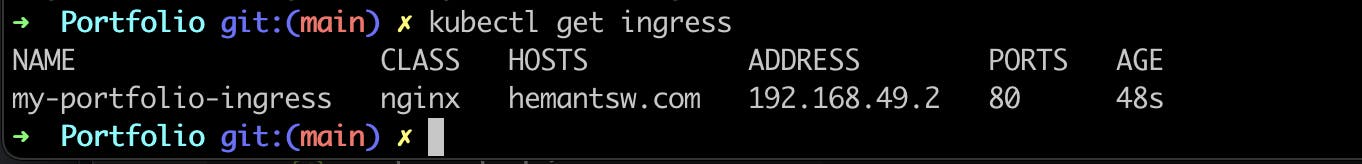
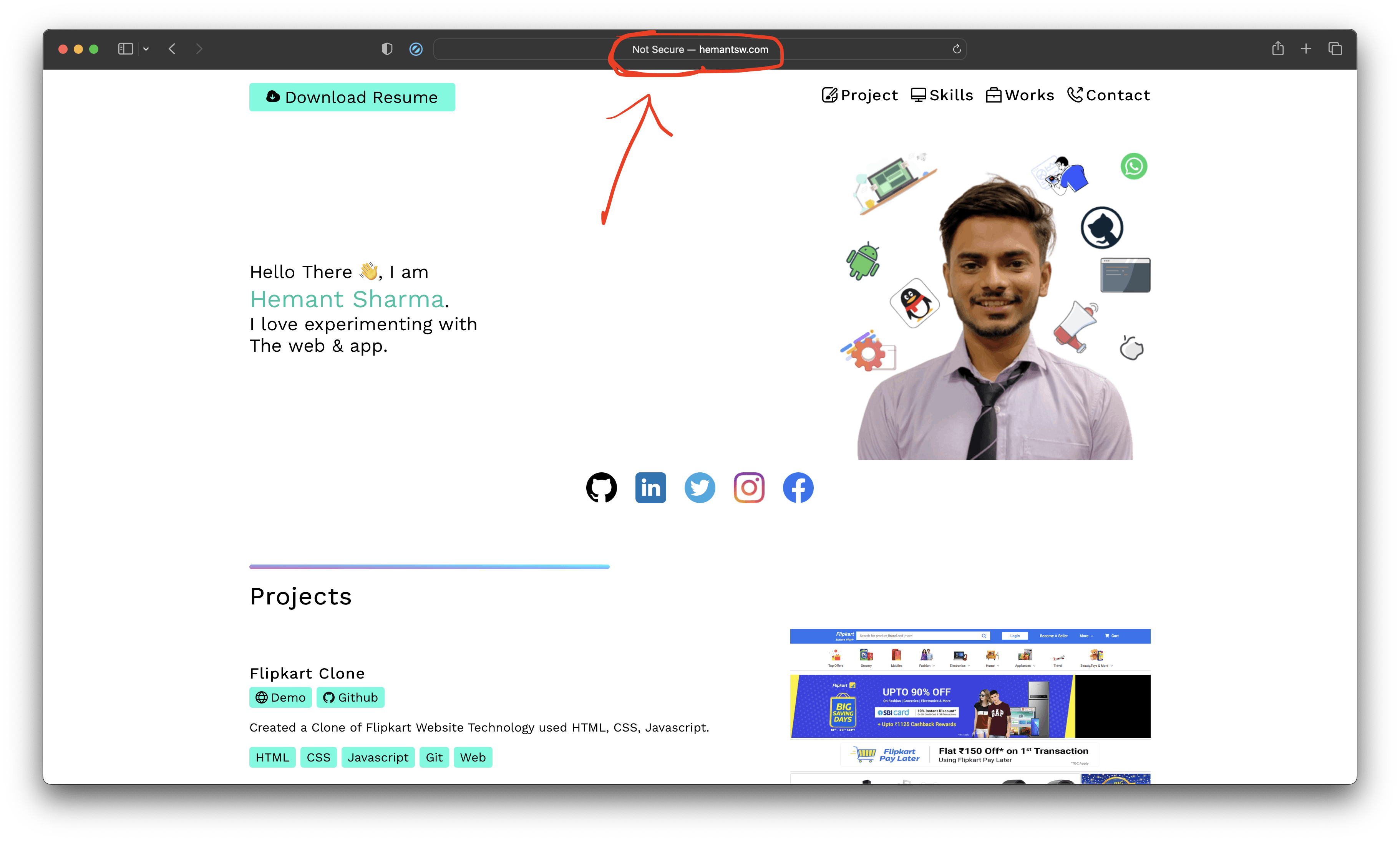
So, when i enter http://hemantsw.com in my browser, I will not able to access the web application because -
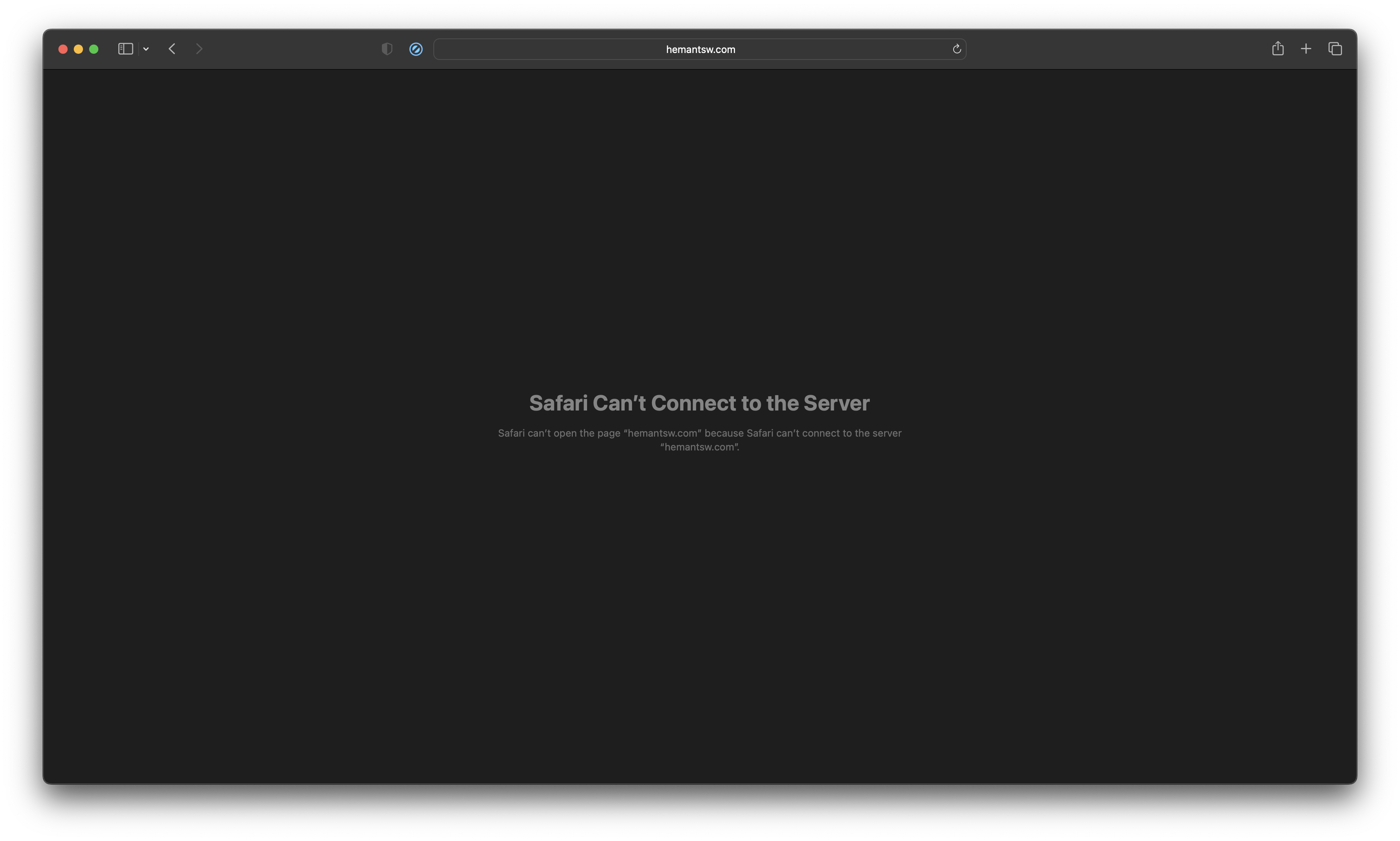
our browser doesn’t know/understand hemantsw.com address. because this domain doesn’t exist. So, we can edit your
/etc/hostsfile.To edit /etc/hosts run this command
sudo vim /etc/hosts
It will ask for password just enter the pass word and Append
127.0.0.1 hemantsw.comto your /etc/hosts file on MacOS (NOTE: Do NOT use the Minikube IP)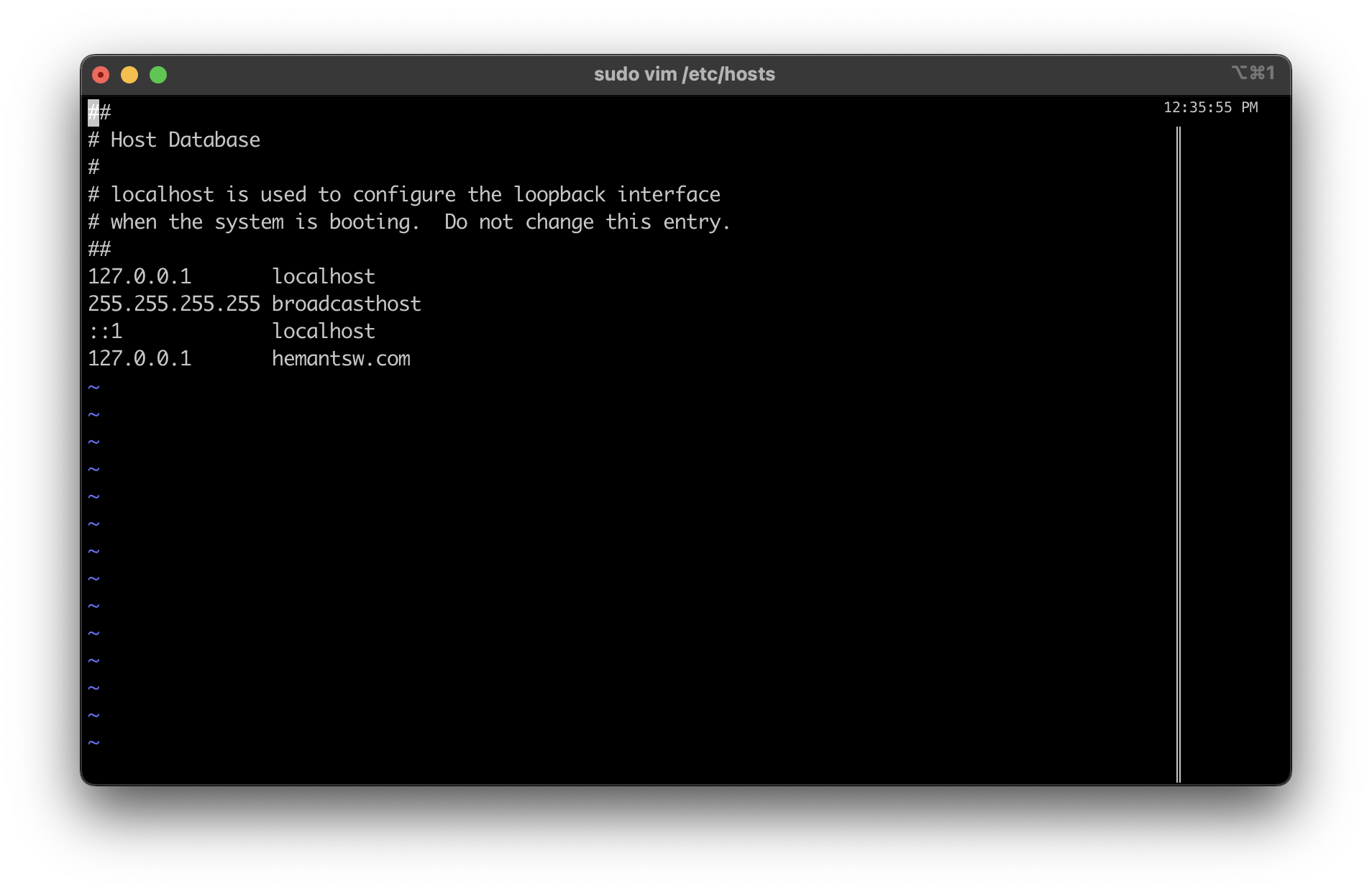
Save this file
Run
minikube tunnel( Keep the window open. After you entered the password there will be no more messages, and the cursor just blinks)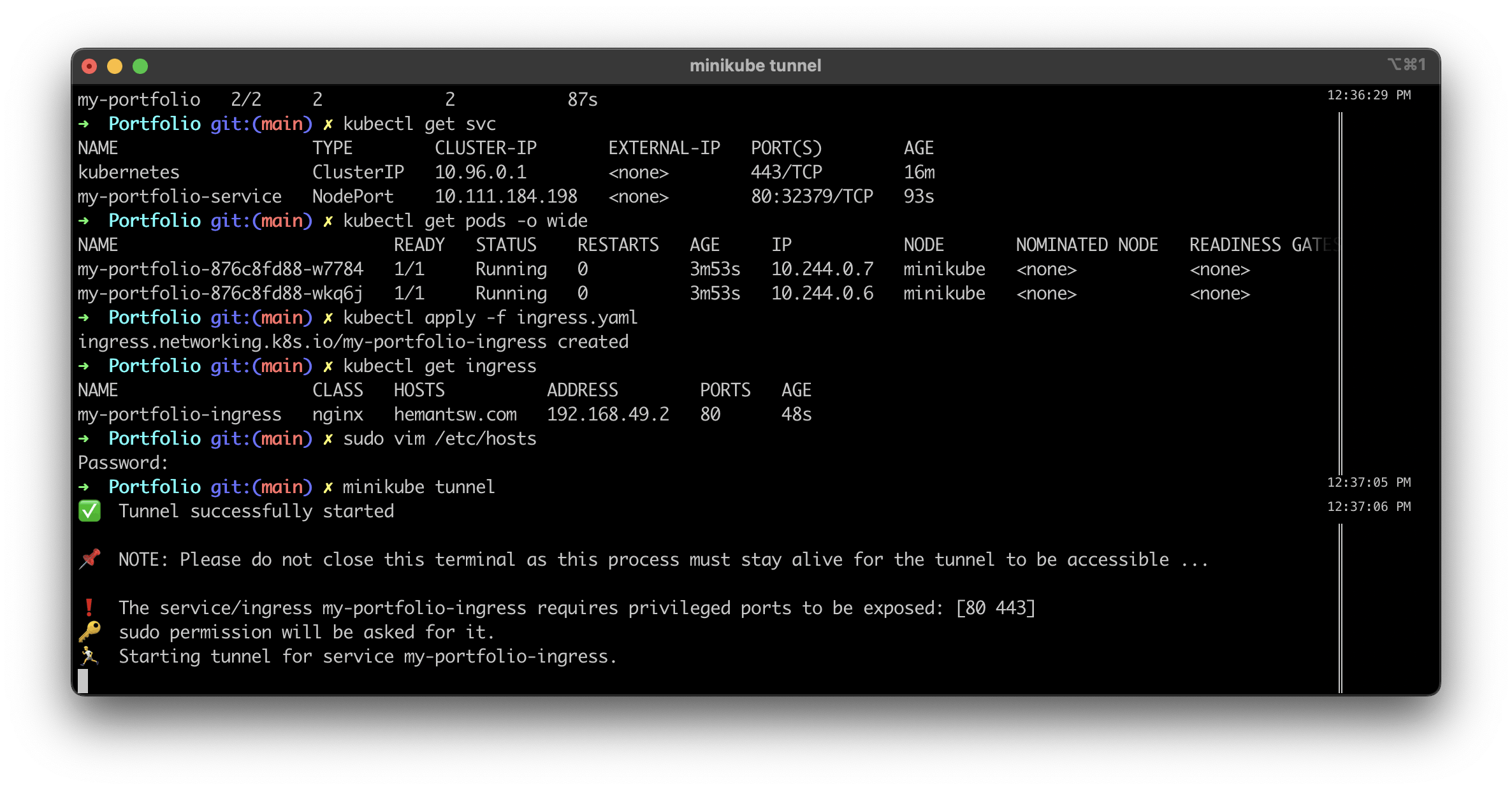
Hit the http://hemantsw.com ( or whatever host you configured in the yaml file) in a browser and it should work